Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
The Weekend Quiz – December 31-January 1, 2016-17 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of modern monetary theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
A rising public debt ratio during a recession is of no concern because it falls once economic growth resumes.
The answer is False.
The primary deficit may not fall when economic growth is positive if discretionary policy changes offset the declining net spending as tax revenue increases and welfare payments fall (the automatic stabilisation).
Under current institutional arrangements, governments around the world voluntarily issue debt into the private bond markets to match $-for-$ their net spending flows in each period. A sovereign government within a fiat currency system does not have to issue any debt and could run continuous fiscal deficits (that is, forever) with a zero public debt.
The reason they is covered in the following blogs – On voluntary constraints that undermine public purpose.
The framework for considering this question is provided by the accounting relationship linking the fiscal flows (spending, taxation and interest servicing) with relevant stocks (base money and government bonds).
This framework has been interpreted by the mainstream macroeconommists as constituting an a priori financial constraint on government spending (more on this soon) and by proponents of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) as an ex post accounting relationship that has to be true in a stock-flow consistent macro model but which carries no particular import other than to measure the changes in stocks between periods. These changes are also not particularly significant within MMT given that a sovereign government is never revenue constrained because it is the monopoly issuer of the currency.
To understand the difference in viewpoint we might usefully start with the mainstream view. The way the mainstream macroeconomics textbooks build this narrative is to draw an analogy between the household and the sovereign government and to assert that the microeconomic constraints that are imposed on individual or household choices apply equally without qualification to the government. The framework for analysing these choices has been called the government budget constraint (GBC) in the literature.
The GBC is in fact an accounting statement relating government spending and taxation to stocks of debt and high powered money. However, the accounting character is downplayed and instead it is presented by mainstream economists as an a priori financial constraint that has to be obeyed. So immediately they shift, without explanation, from an ex post sum that has to be true because it is an accounting identity, to an alleged behavioural constraint on government action.
The GBC is always true ex post but never represents an a priori financial constraint for a sovereign government running a flexible-exchange rate non-convertible currency. That is, the parity between its currency and other currencies floats and the the government does not guarantee to convert the unit of account (the currency) into anything else of value (like gold or silver).
This literature emerged in the 1960s during a period when the neo-classical microeconomists were trying to gain control of the macroeconomic policy agenda by undermining the theoretical validity of the, then, dominant Keynesian macroeconomics. There was nothing particularly progressive about the macroeconomics of the day which is known as Keynesian although as I explain in this blog – Those bad Keynesians are to blame – that is a bit of a misnomer.
Anyway, just as an individual or a household is conceived in orthodox microeconomic theory to maximise utility (real income) subject to their fiscal constraints, this emerging approach also constructed the government as being constrained by a fiscal or “financing” constraint. Accordingly, they developed an analytical framework whereby the fiscal deficits had stock implications – this is the so-called GBC.
So within this model, taxes are conceived as providing the funds to the government to allow it to spend. Further, this approach asserts that any excess in government spending over taxation receipts then has to be “financed” in two ways: (a) by borrowing from the public; and (b) by printing money.
You can see that the approach is a gold standard approach where the quantity of “money” in circulation is proportional (via a fixed exchange price) to the stock of gold that a nation holds at any point in time. So if the government wants to spend more it has to take money off the non-government sector either via taxation of bond-issuance.
However, in a fiat currency system, the mainstream analogy between the household and the government is flawed at the most elemental level. The household must work out the financing before it can spend. The household cannot spend first. The government can spend first and ultimately does not have to worry about financing such expenditure.
From a policy perspective, they believed (via the flawed Quantity Theory of Money) that “printing money” would be inflationary (even though governments do not spend by printing money anyway. So they recommended that deficits be covered by debt-issuance, which they then claimed would increase interest rates by increasing demand for scarce savings and crowd out private investment. All sorts of variations on this nonsense has appeared ranging from the moderate Keynesians (and some Post Keynesians) who claim the “financial crowding out” (via interest rate increases) is moderate to the extreme conservatives who say it is 100 per cent (that is, no output increase accompanies government spending).
So the GBC is the mainstream macroeconomics framework for analysing these “financing” choices and it says that the fiscal deficit in year t is equal to the change in government debt (ΔB) over year t plus the change in high powered money (ΔH) over year t. If we think of this in real terms (rather than monetary terms), the mathematical expression of this is written as:
which you can read in English as saying that Budget deficit (BD) = Government spending (G) – Tax receipts (T) + Government interest payments (rBt-1), all in real terms.
However, this is merely an accounting statement. It has to be true if things have been added and subtracted properly in accounting for the dealings between the government and non-government sectors.
In mainstream economics, money creation is erroneously depicted as the government asking the central bank to buy treasury bonds which the central bank in return then prints money. The government then spends this money. This is called debt monetisation and we have shown in the Deficits 101 series how this conception is incorrect. Anyway, the mainstream claims that if the government is willing to increase the money growth rate it can finance a growing deficit but also inflation because there will be too much money chasing too few goods! But an economy constrained by deficient demand (defined as demand below the full employment level) responds to a nominal impulse by expanding real output not prices.
But because they believe that inflation is inevitable if “printing money” occurs, mainstream economists recommend that governments use debt issuance to “finance” their deficits. But then they scream that this will merely require higher future taxes. Why should taxes have to be increased?
Well the textbooks are full of elaborate models of debt pay-back, debt stabilisation etc which all “prove” (not!) that the legacy of past deficits is higher debt and to stabilise the debt, the government must eliminate the deficit which means it must then run a primary surplus equal to interest payments on the existing debt.
Nothing is included about the swings and roundabouts provided by the automatic stabilisers as the results of the deficits stimulate private activity and welfare spending drops and tax revenue rises automatically in line with the increased economic growth. Most orthodox models are based on the assumption of full employment anyway, which makes them nonsensical depictions of the real world.
More sophisticated mainstream analyses focus on the ratio of debt to GDP rather than the level of debt per se. They come up with the following equation – nothing that they now disregard the obvious opportunity presented to the government via ΔH. So in the following model all net public spending is covered by new debt-issuance (even though in a fiat currency system no such financing is required).
Accordingly, the change in the public debt ratio is:
The change in the debt ratio is the sum of two terms on the right-hand side: (a) the difference between the real interest rate (r) and the GDP growth rate (g) times the initial debt ratio; and (b) the ratio of the primary deficit (G-T) to GDP.
A growing economy can absorb more debt and keep the debt ratio constant. For example, if the primary deficit is zero, debt increases at a rate r but the debt ratio increases at r – g.
So a change in the change in the debt ratio is the sum of two terms on the right-hand side: (a) the difference between the real interest rate (r) and the GDP growth rate (g) times the initial debt ratio; and (b) the ratio of the primary deficit (G-T) to GDP.
As we noted a growing economy can absorb more debt and keep the debt ratio constant. For example, if the primary deficit is zero, debt increases at a rate r but the debt ratio increases at r – g.
Consider the following table which simulates two different scenarios. Case A shows a real interest rate of zero and a steadily increasing annual GDP growth rate across 10 years. The initial public debt ratio is 100 per cent (so well over the level Reinhart and Rogoff claim is the point of no return and insolvency is pending). The fiscal deficit is also simulated to be 5 per cent of GDP then reduces as the GDP growth induce the automatic stabilisers. It then reaches a steady 2 per cent per annum which might be sufficient to support the saving intentions of the non-government sector while still promoting steady economic growth.
You can see that the even with a continuous deficit, the public debt ratio declines steadily and would continue to do so as the growth continued. The central bank could of-course cut the nominal interest rate to speed the contraction in the debt ratio although I would not undertake that policy change for that reason.
In Case B we assume that the government stops issuing debt with everything else the same. The public debt ratio drops very quickly under this scenario.
However, should the real interest rate exceed the economic growth rate, then unless the primary fiscal balance offsets the rising interest payments as percent of GDP, then the public debt ratio will rise.
The only concern I would have in this situation does not relate to the rising ratio. Focusing on the cause should be the policy concern. If the real economy is faltering because interest rates are too high or more likely because the primary fiscal deficit is too low then the rising public debt ratio is just telling us that the central bank should drop interest rates or the treasury should increase the discretionary component of the fiscal balance.
In general though, the public debt ratio is a relatively uninteresting macroeconomic figure and should be disregarded. If the government is intent on promoting growth, then the primary deficit ratio and the public debt ratio will take care of themselves.
You may be interested in reading these blogs which have further information on this topic:
- On voluntary constraints that undermine public purpose
- Deficits 101 series
- Questions and answers 1
- Will we really pay higher taxes?
- Will we really pay higher interest rates?
Question 2:
Only one of the following propositions is possible (with all balances expressed as a per cent of GDP) – a nation can run a current account deficit:
- Accompanied by a government sector surplus of equal size, while the private domestic sector spends less than it earns.
- Accompanied by a government sector surplus of equal size, while the private domestic sector spends more than it earns.
- Accompanied by a government sector surplus that is larger, while the private domestic sector spends less than it earns.
- None of the above are possible as they all defy the sectoral balances accounting identity.
The best answer is the second option – A nation can run a current account deficit accompanied by a government sector surplus of equal size, while the private domestic sector spends more than it earns.
This is a question about the sectoral balances – the government fiscal balance, the external balance and the private domestic balance – that have to always add to zero because they are derived as an accounting identity from the national accounts.
To refresh your memory the sectoral balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective, we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
Expression (1) tells us that total income in the economy per period will be exactly equal to total spending from all sources of expenditure.
We also have to acknowledge that financial balances of the sectors are impacted by net government taxes (T) which includes all taxes and transfer and interest payments (the latter are not counted independently in the expenditure Expression (1)).
Further, as noted above the trade account is only one aspect of the financial flows between the domestic economy and the external sector. we have to include net external income flows (FNI).
Adding in the net external income flows (FNI) to Expression (2) for GDP we get the familiar gross national product or gross national income measure (GNP):
(2) GNP = C + I + G + (X – M) + FNI
To render this approach into the sectoral balances form, we subtract total taxes and transfers (T) from both sides of Expression (3) to get:
(3) GNP – T = C + I + G + (X – M) + FNI – T
Now we can collect the terms by arranging them according to the three sectoral balances:
(4) (GNP – C – T) – I = (G – T) + (X – M + FNI)
The the terms in Expression (4) are relatively easy to understand now.
The term (GNP – C – T) represents total income less the amount consumed less the amount paid to government in taxes (taking into account transfers coming the other way). In other words, it represents private domestic saving.
The left-hand side of Equation (4), (GNP – C – T) – I, thus is the overall saving of the private domestic sector, which is distinct from total household saving denoted by the term (GNP – C – T).
In other words, the left-hand side of Equation (4) is the private domestic financial balance and if it is positive then the sector is spending less than its total income and if it is negative the sector is spending more than it total income.
The term (G – T) is the government financial balance and is in deficit if government spending (G) is greater than government tax revenue minus transfers (T), and in surplus if the balance is negative.
Finally, the other right-hand side term (X – M + FNI) is the external financial balance, commonly known as the current account balance (CAD). It is in surplus if positive and deficit if negative.
In English we could say that:
The private financial balance equals the sum of the government financial balance plus the current account balance.
We can re-write Expression (6) in this way to get the sectoral balances equation:
(5) (S – I) = (G – T) + CAD
which is interpreted as meaning that government sector deficits (G – T > 0) and current account surpluses (CAD > 0) generate national income and net financial assets for the private domestic sector.
Conversely, government surpluses (G – T < 0) and current account deficits (CAD < 0) reduce national income and undermine the capacity of the private domestic sector to add financial assets.
Expression (5) can also be written as:
(6) [(S – I) – CAD] = (G – T)
where the term on the left-hand side [(S – I) – CAD] is the non-government sector financial balance and is of equal and opposite sign to the government financial balance.
This is the familiar MMT statement that a government sector deficit (surplus) is equal dollar-for-dollar to the non-government sector surplus (deficit).
The sectoral balances equation says that total private savings (S) minus private investment (I) has to equal the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)) plus net income transfers.
All these relationships (equations) hold as a matter of accounting and not matters of opinion.
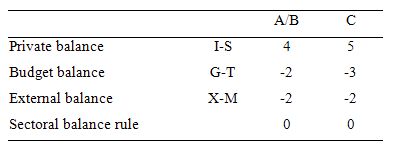
The following Table represents the three options in percent of GDP terms.
To aid interpretation remember that (I-S) > 0 means that the private domestic sector is spending more than they are earning; that (G-T) < 0 means that the government is running a surplus because T > G; and (X-M) < 0 means the external position is in deficit because imports are greater than exports.
The first two possibilities we might call A and B:
A: A nation can run a current account deficit accompanied by a government sector surplus of equal size, while the private domestic sector spends less than it earns.
B: A nation can run a current account deficit accompanied by a government sector surplus of equal size, while the private domestic sector spends more than it earns.
So Option A says the private domestic sector is saving overall, whereas Option B say the private domestic sector is dis-saving (increasing indebtedness). These options are captured in the first column of the Table. So the arithmetic example depicts an external sector deficit of 2 per cent of GDP and an offsetting fiscal surplus of 2 per cent of GDP.
You can see that the private sector balance is positive (that is, the sector is spending more than they are earning – Investment is greater than Saving – and has to be equal to 4 per cent of GDP.
Given that the only proposition that can be true is:
B: A nation can run a current account deficit accompanied by a government sector surplus of equal size, while the private domestic sector spends more than it earns.
Column 2 in the Table captures Option C:
C: A nation can run a current account deficit accompanied by a government sector surplus that is larger, while the private domestic sector spends less than it earns.
So the current account deficit is equal to 2 per cent of GDP while the surplus is now larger at 3 per cent of GDP. You can see that the private domestic deficit rises to 5 per cent of GDP to satisfy the accounting rule that the balances sum to zero.
The final option available is:
D: None of the above are possible as they all defy the sectoral balances accounting identity.
It cannot be true because as the Table data shows the rule that the sectoral balances add to zero because they are an accounting identity is satisfied in both cases.
So if the G is spending less than it is “earning” and the external sector is adding less income (X) than it is absorbing spending (M), then the other spending components must be greater than total income
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Barnaby, better to walk before we run
- Stock-flow consistent macro models
- Norway and sectoral balances
- The OECD is at it again!
Question 3:
The expansionary impact of deficit spending on aggregate demand will be lower when the government matches its fiscal deficit with debt-issuance compared to a situation where it issues no debt.
The answer is False.
The mainstream macroeconomic textbooks all have a chapter on fiscal policy (and it is often written in the context of the so-called IS-LM model but not always).
The chapters always introduces the so-called Government Budget Constraint (as explained above) that alleges that governments have to “finance” all spending either through taxation; debt-issuance; or money creation. The writer fails to understand that government spending is performed in the same way irrespective of the accompanying monetary operations.
They claim that money creation (borrowing from central bank) is inflationary while the latter (private bond sales) is less so. These conclusions are based on their erroneous claim that “money creation” adds more to aggregate demand than bond sales, because the latter forces up interest rates which crowd out some private spending.
All these claims are without foundation in a fiat monetary system and an understanding of the banking operations that occur when governments spend and issue debt helps to show why.
So what would happen if a sovereign, currency-issuing government (with a flexible exchange rate) ran a fiscal deficit without issuing debt?
Like all government spending, the Treasury would credit the reserve accounts held by the commercial bank at the central bank. The commercial bank in question would be where the target of the spending had an account. So the commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a deposit would be made.
The transactions are clear: The commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a new deposit has been made. Further, the target of the fiscal initiative enjoys increased assets (bank deposit) and net worth (a liability/equity entry on their balance sheet).
Taxation does the opposite and so a deficit (spending greater than taxation) means that reserves increase and private net worth increases.
This means that there are likely to be excess reserves in the “cash system” which then raises issues for the central bank about its liquidity management. The aim of the central bank is to “hit” a target interest rate and so it has to ensure that competitive forces in the interbank market do not compromise that target.
When there are excess reserves there is downward pressure on the overnight interest rate (as banks scurry to seek interest-earning opportunities), the central bank then has to sell government bonds to the banks to soak the excess up and maintain liquidity at a level consistent with the target. Some central banks offer a return on overnight reserves which reduces the need to sell debt as a liquidity management operation.
There is no sense that these debt sales have anything to do with “financing” government net spending. The sales are a monetary operation aimed at interest-rate maintenance. So M1 (deposits in the non-government sector) rise as a result of the deficit without a corresponding increase in liabilities. It is this result that leads to the conclusion that that deficits increase net financial assets in the non-government sector.
What would happen if there were bond sales? All that happens is that the banks reserves are reduced by the bond sales but this does not reduce the deposits created by the net spending. So net worth is not altered. What is changed is the composition of the asset portfolio held in the non-government sector.
The only difference between the Treasury “borrowing from the central bank” and issuing debt to the private sector is that the central bank has to use different operations to pursue its policy interest rate target. If it debt is not issued to match the deficit then it has to either pay interest on excess reserves (which most central banks are doing now anyway) or let the target rate fall to zero (the Japan solution).
There is no difference to the impact of the deficits on net worth in the non-government sector.
Mainstream economists would say that by draining the reserves, the central bank has reduced the ability of banks to lend which then, via the money multiplier, expands the money supply.
However, the reality is that:
- Building bank reserves does not increase the ability of the banks to lend.
- The money multiplier process so loved by the mainstream does not describe the way in which banks make loans.
- Inflation is caused by aggregate demand growing faster than real output capacity. The reserve position of the banks is not functionally related with that process.
So the banks are able to create as much credit as they can find credit-worthy customers to hold irrespective of the operations that accompany government net spending.
This doesn’t lead to the conclusion that deficits do not carry an inflation risk. All components of aggregate demand carry an inflation risk if they become excessive, which can only be defined in terms of the relation between spending and productive capacity.
It is totally fallacious to think that private placement of debt reduces the inflation risk. It does not.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:

This Post Has 0 Comments