Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
The Weekend Quiz – January 21-22, 2017 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of modern monetary theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
A program of fiscal austerity which yields a fiscal surplus will always undermine attempts by the private domestic sector to save overall when the nation’s exports are less than the sum of their imports and net income flows.
The answer is True.
Fact – when a nation exports less than they import (including net income flows) we say they have an external deficit (current account deficit).
This is a question about the sectoral balances – the government fiscal balance, the external balance and the private domestic balance – that have to always add to zero because they are derived as an accounting identity from the national accounts. The balances reflect the underlying economic behaviour in each sector which is interdependent – given this is a macroeconomic system we are considering.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
(1) GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
Expression (1) tells us that total income in the economy per period will be exactly equal to total spending from all sources of expenditure.
We also have to acknowledge that financial balances of the sectors are impacted by net government taxes (T) which includes all tax revenue minus total transfer and interest payments (the latter are not counted independently in the expenditure Expression (1)).
Further, as noted above the trade account is only one aspect of the financial flows between the domestic economy and the external sector. we have to include net external income flows (FNI).
Adding in the net external income flows (FNI) to Expression (2) for GDP we get the familiar gross national product or gross national income measure (GNP):
(2) GNP = C + I + G + (X – M) + FNI
To render this approach into the sectoral balances form, we subtract total net taxes (T) from both sides of Expression (3) to get:
(3) GNP – T = C + I + G + (X – M) + FNI – T
Now we can collect the terms by arranging them according to the three sectoral balances:
(4) (GNP – C – T) – I = (G – T) + (X – M + FNI)
The the terms in Expression (4) are relatively easy to understand now.
The term (GNP – C – T) represents total income less the amount consumed less the amount paid to government in taxes (taking into account transfers coming the other way). In other words, it represents private domestic saving.
The left-hand side of Equation (4), (GNP – C – T) – I, thus is the overall saving of the private domestic sector, which is distinct from total household saving denoted by the term (GNP – C – T).
In other words, the left-hand side of Equation (4) is the private domestic financial balance and if it is positive then the sector is spending less than its total income and if it is negative the sector is spending more than it total income.
The term (G – T) is the government financial balance and is in deficit if government spending (G) is greater than government tax revenue minus transfers (T), and in surplus if the balance is negative.
Finally, the other right-hand side term (X – M + FNI) is the external financial balance, commonly known as the current account balance (CAD). It is in surplus if positive and deficit if negative.
In English we could say that:
The private financial balance equals the sum of the government financial balance plus the current account balance.
We can re-write Expression (6) in this way to get the sectoral balances equation:
(5) (S – I) = (G – T) + CAD
which is interpreted as meaning that government sector deficits (G – T > 0) and current account surpluses (CAD > 0) generate national income and net financial assets for the private domestic sector.
Conversely, government surpluses (G – T < 0) and current account deficits (CAD < 0) reduce national income and undermine the capacity of the private domestic sector to add financial assets.
Expression (5) can also be written as:
(6) [(S – I) – CAD] = (G – T)
where the term on the left-hand side [(S – I) – CAD] is the non-government sector financial balance and is of equal and opposite sign to the government financial balance.
This is the familiar MMT statement that a government sector deficit (surplus) is equal dollar-for-dollar to the non-government sector surplus (deficit).
The sectoral balances equation says that total private savings (S) minus private investment (I) has to equal the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)) plus net income transfers.
All these relationships (equations) hold as a matter of accounting and not matters of opinion.
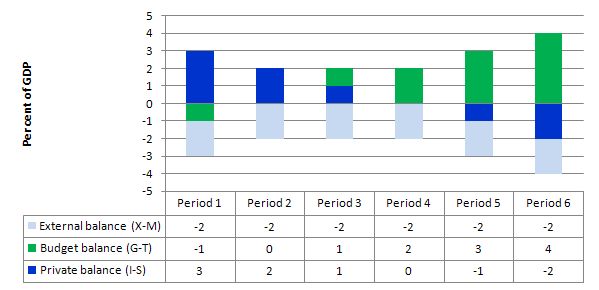
The following graph with accompanying data table lets you see the evolution of the balances expressed in terms of percent of GDP. I have held the external deficit constant at 2 per cent of GDP (which is artificial because as economic activity changes imports also rise and fall).
To aid interpretation remember that (I-S) > 0 means that the private domestic sector is spending more than they are earning; that (G-T) < 0 means that the government is running a surplus because T > G; and (X-M) < 0 means the external position is in deficit because imports plus net income flows are greater than exports. The net income flows are assumed to be negative (given the way I have constructed the external balance information).
If we assume these Periods are average positions over the course of each business cycle (that is, Period 1 is a separate business cycle to Period 2 etc).
In Period 1, there is an external deficit (2 per cent of GDP), a fiscal surplus of 1 per cent of GDP and the private sector is in deficit (I > S) to the tune of 3 per cent of GDP.
In Period 2, as the government fiscal outcome enters balance (presumably the government increased spending or cut taxes or the automatic stabilisers were working), the private domestic deficit narrows and now equals the external deficit. This is the case that the question is referring to.
This provides another important rule with the deficit terorists typically overlook – that if a nation records an average external deficit over the course of the business cycle (peak to peak) and you succeed in balancing the public fiscal balance then the private domestic sector will be in deficit equal to the external deficit. That means, the private sector is increasingly building debt to fund its “excess expenditure”. That conclusion is inevitable when a fiscal balance is accompanied by an external deficit. It could never be a viable fiscal rule.
With an external deficit, it is impossible for both the government and the private domestic sector to reduce their overall debt levels by spending less than they earn.
In Periods 3 and 4, the fiscal deficit rises from balance to 1 to 2 per cent of GDP and the private domestic balance moves towards surplus. At the end of Period 4, the private sector is spending as much as they earning.
Periods 5 and 6 show the benefits of fiscal deficits when there is an external deficit. The private sector now is able to generate surpluses overall (that is, save as a sector) as a result of the public deficit.
So what is the economics that underpin these different situations?
If the nation is running an external deficit it means that the contribution to aggregate demand from the external sector is negative – that is net drain of spending – dragging output down.
The external deficit also means that foreigners are increasing financial claims denominated in the local currency. Given that exports represent a real cost and imports a real benefit, the motivation for a nation running a net exports surplus (the exporting nation in this case) must be to accumulate financial claims (assets) denominated in the currency of the nation running the external deficit.
A fiscal surplus also means the government is spending less than it is “earning” and that puts a drag on aggregate demand and constrains the ability of the economy to grow.
In these circumstances, for income to be stable, the private domestic sector has to spend more than they earn.
You can see this by going back to the aggregate demand relations above. For those who like simple algebra we can manipulate the aggregate demand model to see this more clearly.
Y = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that the total national income (Y or GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
So if the G is spending less than it is “earning” and the external sector is adding less income (X) than it is absorbing spending (M), then the other spending components must be greater than total income.
Only when the government fiscal deficit supports aggregate demand at income levels which permit the private sector to save out of that income will the latter achieve its desired outcome. At this point, income and employment growth are maximised and private debt levels will be stable.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Barnaby, better to walk before we run
- Stock-flow consistent macro models
- Norway and sectoral balances
- The OECD is at it again!
Question 2:
The more funds that commercial banks have on account with the central bank the greater is their capacity to provide loans to customers
The answer is False.
This is a question about whether you understand the flawed concept of the money multiplier and bank reserves.
Mainstream macroeconomics textbooks present a flawed depiction of the credit-creation capacity of commercial banks. The concept of the money multiplier is at the centre of this analysis and posits that the multiplier m transmits changes in the so-called monetary base (MB) (the sum of bank reserves and currency at issue) into changes in the money supply (M). The chapters on money usually present some arcane algebra which is deliberately designed to impart a sense of gravitas or authority to the students who then mindlessly ape what is in the textbook.
They rehearse several times in their undergraduate courses (introductory and intermediate macroeconomics; money and banking; monetary economics etc) the mantra that the money multiplier is usually expressed as the inverse of the required reserve ratio plus some other novelties relating to preferences for cash versus deposits by the public.
Accordingly, the students learn that if the central bank told private banks that they had to keep 10 per cent of total deposits as reserves then the required reserve ratio (RRR) would be 0.10 and m would equal 1/0.10 = 10. More complicated formulae are derived when you consider that people also will want to hold some of their deposits as cash. But these complications do not add anything to the story.
The formula for the determination of the money supply is: M = m x MB. So if a $1 is newly deposited in a bank, the money supply will rise (be multiplied) by $10 (if the RRR = 0.10). The way this multiplier is alleged to work is explained as follows (assuming the bank is required to hold 10 per cent of all deposits as reserves):
- A person deposits say $100 in a bank.
- To make money, the bank then loans the remaining $90 to a customer.
- They spend the money and the recipient of the funds deposits it with their bank.
- That bank then lends 0.9 times $90 = $81 (keeping 0.10 in reserve as required).
- And so on until the loans become so small that they dissolve to zero
None of this is accurate in terms of depicting how the banks make loans. It is an important device for the mainstream because it implies that banks take deposits to get funds which they can then on-lend. But prudential regulations require they keep a little in reserve. So we get this credit creation process ballooning out due to the fractional reserve requirements.
The money multiplier myth also leads students to think that as the central bank can control the monetary base then it can control the money supply. Further, given that inflation is allegedly the result of the money supply growing too fast then the blame is sheeted hometo the “government”. This leads to claims that if the government runs a fiscal deficit then it has to issue bonds to avoid causing hyperinflation. Nothing could be further from the truth.
That is nothing like the way the banking system operates in the real world. The idea that the monetary base (the sum of bank reserves and currency) leads to a change in the money supply via some multiple is not a valid representation of the way the monetary system operates.
First, the central bank does not have the capacity to control the money supply in a modern monetary system. In the world we live in, bank loans create deposits and are made without reference to the reserve positions of the banks. The bank then ensures its reserve positions are legally compliant as a separate process knowing that it can always get the reserves from the central bank. The only way that the central bank can influence credit creation in this setting is via the price of the reserves it provides on demand to the commercial banks.
Second, this suggests that the decisions by banks to lend may be influenced by the price of reserves rather than whether they have sufficient reserves. They can always get the reserves that are required at any point in time at a price, which may be prohibitive.
Third, the money multiplier story has the central bank manipulating the money supply via open market operations. So they would argue that the central bank might buy bonds to the public to increase the money base and then allow the fractional reserve system to expand the money supply. But a moment’s thought will lead you to conclude this would be futile unless (as in Question 3 a support rate on excess reserves equal to the current policy rate was being paid).
Why? The open market purchase would increase bank reserves and the commercial banks, in lieu of any market return on the overnight funds, would try to place them in the interbank market. Of-course, any transactions at this level (they are horizontal) net to zero so all that happens is that the excess reserve position of the system is shuffled between banks. But in the process the interbank return would start to fall and if the process was left to resolve, the overnight rate would fall to zero and the central bank would lose control of its monetary policy position (unless it was targetting a zero interest rate).
In lieu of a support rate equal to the target rate, the central bank would have to sell bonds to drain the excess reserves. The same futility would occur if the central bank attempted to reduce the money supply by instigating an open market sale of bonds.
In all cases, the central bank cannot influence the money supply in this way.
Fourth, given that the central bank adds reserves on demand to maintain financial stability and this process is driven by changes in the money supply as banks make loans which create deposits. Banks do not initially need reserves to lend. Reserves are used to facilitate the integrity of the clearing house (payments system). The links below provide more in-depth analysis of that point.
So the operational reality is that the dynamics of the monetary base (MB) are driven by the changes in the money supply which is exactly the reverse of the causality presented by the monetary multiplier.
So in fact we might write MB = M/m, where m is a divisor.
You might like to read these blogs for further information:
- Teaching macroeconomics students the facts
- Lost in a macroeconomics textbook again
- Lending is capital- not reserve-constrained
- Oh no … Bernanke is loose and those greenbacks are everywhere
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- 100-percent reserve banking and state banks
- Money multiplier and other myths
Question 3:
If governments sought funding from the central bank for their net spending (deficits) rather than private bond markets then the inflation risk of such spending would remain unchanged.
The answer is True.
The mainstream macroeconomic textbooks all have a chapter on fiscal policy (and it is often written in the context of the so-called IS-LM model but not always).
The chapters always introduces the so-called Government Budget Constraint (as explained above) that alleges that governments have to “finance” all spending either through taxation; debt-issuance; or money creation. The writer fails to understand that government spending is performed in the same way irrespective of the accompanying monetary operations.
They claim that money creation (borrowing from central bank) is inflationary while the latter (private bond sales) is less so. These conclusions are based on their erroneous claim that “money creation” adds more to aggregate demand than bond sales, because the latter forces up interest rates which crowd out some private spending.
All these claims are without foundation in a fiat monetary system and an understanding of the banking operations that occur when governments spend and issue debt helps to show why.
So what would happen if a sovereign, currency-issuing government (with a flexible exchange rate) ran a fiscal deficit without issuing debt?
Like all government spending, the Treasury would credit the reserve accounts held by the commercial bank at the central bank. The commercial bank in question would be where the target of the spending had an account. So the commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a deposit would be made.
The transactions are clear: The commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a new deposit has been made. Further, the target of the fiscal initiative enjoys increased assets (bank deposit) and net worth (a liability/equity entry on their balance sheet).
Taxation does the opposite and so a deficit (spending greater than taxation) means that reserves increase and private net worth increases.
This means that there are likely to be excess reserves in the “cash system” which then raises issues for the central bank about its liquidity management. The aim of the central bank is to “hit” a target interest rate and so it has to ensure that competitive forces in the interbank market do not compromise that target.
When there are excess reserves there is downward pressure on the overnight interest rate (as banks scurry to seek interest-earning opportunities), the central bank then has to sell government bonds to the banks to soak the excess up and maintain liquidity at a level consistent with the target. Some central banks offer a return on overnight reserves which reduces the need to sell debt as a liquidity management operation.
There is no sense that these debt sales have anything to do with “financing” government net spending. The sales are a monetary operation aimed at interest-rate maintenance. So M1 (deposits in the non-government sector) rise as a result of the deficit without a corresponding increase in liabilities. It is this result that leads to the conclusion that that deficits increase net financial assets in the non-government sector.
What would happen if there were bond sales? All that happens is that the banks reserves are reduced by the bond sales but this does not reduce the deposits created by the net spending. So net worth is not altered. What is changed is the composition of the asset portfolio held in the non-government sector.
The only difference between the Treasury “borrowing from the central bank” and issuing debt to the private sector is that the central bank has to use different operations to pursue its policy interest rate target. If it debt is not issued to match the deficit then it has to either pay interest on excess reserves (which most central banks are doing now anyway) or let the target rate fall to zero (the Japan solution).
There is no difference to the impact of the deficits on net worth in the non-government sector.
Mainstream economists would say that by draining the reserves, the central bank has reduced the ability of banks to lend which then, via the money multiplier, expands the money supply.
However, the reality is that:
- Building bank reserves does not increase the ability of the banks to lend.
- The money multiplier process so loved by the mainstream does not describe the way in which banks make loans.
- Inflation is caused by aggregate demand growing faster than real output capacity. The reserve position of the banks is not functionally related with that process.
So the banks are able to create as much credit as they can find credit-worthy customers to hold irrespective of the operations that accompany government net spending.
This doesn’t lead to the conclusion that deficits do not carry an inflation risk. All components of aggregate demand carry an inflation risk if they become excessive, which can only be defined in terms of the relation between spending and productive capacity.
It is totally fallacious to think that private placement of debt reduces the inflation risk. It does not.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
- Why history matters
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- The complacent students sit and listen to some of that
- Saturday Quiz – February 27, 2010 – answers and discussion
That is enough for today!
(c) Copyright 2017 William Mitchell. All Rights Reserved.
Why is it that sectoral balances are, or seem, not to be accepted by mainstream economics?
Richard Holden, in the recent TC blog was disparaging of the concept, and I have had refusals to accept elsewhere outside MMT. If it is an accounting identity then why is it unacceptable? It certainly doesn’t make sense.
I have the same question as John Doyle. I mean it seems that many of them don’t even act as though GDP=C+I+G+(X-M). They always will acknowledge that it does if pressed, but then start blathering about identities and definitions and how they cant be used for any type of reasoning whatsoever. Which is just stupid if you ask me. Why cant economists make some reasonable guesses about likely economic behavior within the constraints of these identities?
Jerry and John – All Richard Holden does is stuff about with ridiculous mathematics and rational expectations models to explain the behaviour of a species which never has and never will exist.
John Doyle, I found the answer to my question (and maybe yours) here-
https://billmitchell.org/blog/?p=32396
As is often the case, Bill has already written the answer to my question.
Alan Dunn, I agree.